Autoclave: Definition, Meaning, Principle, Applications, and Uses:
"Autoclave" do you have too much information about him? Here it will be short about everything and of course in order. This will help you learn something new or structure what you already have. Below we will tell you what an is autoclave, How it works, and Its application.
Autoclave Definition:
- An autoclave is a device that uses steam to kill harmful bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores present on an object.
- Autoclaves are machines that use pressurized steam to kill or eliminate microorganisms from an object.
Principle of Autoclave:
- Before the invention of the autoclave in the 19th century, medical instruments were sterilized by immersion in boiled water.
- But some microbes survive the process, so hotter equipment is needed to solve the problem.
- Steam is an ideal medium.
- Steam is pressurized in an autoclave and becomes hotter than boiling water, enough to kill heat-resistant microorganisms.
- The principle of operation of the autoclave is to heat water to a temperature of over 100 degrees. Under normal conditions, this cannot be achieved, because. when this temperature is reached, the water does not heat up further but simply evaporates.
- When the water reaches a temperature of 90 degrees, it begins to evaporate, but because the device is sealed, the steam does not come out.
- As a result of the conversion of moisture into gas, excess pressure is created. At some point, evaporation stops.
- With an increase in pressure inside the vessel, the temperature of the water also rises (up to 300-500 degrees in some autoclaves).
- At a temperature of 121 degrees, sterilization of products begins - the destruction of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and even spores.
History of Autoclave:
- In 1679 Papin invented his steam digester (pressure cooker), a closed vessel with a tightly fitting lid that confines the steam until a high pressure is generated.
- In 1809, Nicolas Appert came up with a special way of preserving food in airtight jars using high temperatures. This method became the progenitor of modern autoclaves.
- In 1879, Charles Chamberlain invented the first true autoclave - a hermetic device in which the necessary pressure was created when heated. He used his device only in chemical experiments and in medicine to sterilize instruments.
- In 1953, the first industrial textile autoclave appeared, created by the French company Lagarde.
- In 1972, the same company developed the first autoclave for food sterilization.
- In the 80s, autoclaves for home canning appeared.
- The first autoclaves for food preservation were electric, later gas appeared.
Fig: Autoclave Diagram in Microbiology
What is Autoclave?
- Autoclaves are machines that use pressurized steam to kill or eliminate microorganisms from an object.
- An autoclave is also known as a high-pressure steam sterilizer.
The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879.- At that time, researchers began to understand the advantages of aseptic surgery, and doctors needed a more reliable method of sterilization than an open flame.
- The autoclave is considered one of the efficient methods of moist heat sterilization.
- Steam is the sterilizing agent of the autoclave.
- Generally, the autoclave can be divided into portable sterilizers and vertical autoclaves.
- Autoclaves vary in size, shape, and function.
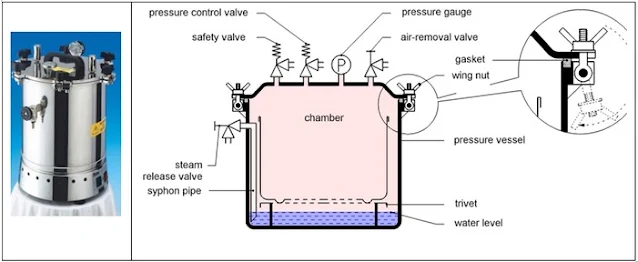
- It mainly consists of a sealable barrel, pressure gauge, exhaust valve, safety valve, electric heating wire, etc.
- An autoclave is used for disinfection and sterilization of culture medium, medical equipment, glassware, etc.
- It sterilizes solids, liquids, hollows, and instruments of all shapes and sizes.
- A very basic pressure cooker is similar to an autoclave. Although their basic functions are also similar at ground level. Both use the power of steam to kill germs, spores, and bacteria that are resistant to boiling water and are strong cleaners.
- Autoclave sterilizers are widely used in colleges and universities, medical and health care, food chemical industry, scientific research, and other units to sterilize equipment.
Autoclave Diagram:
Fig: Autoclave diagram with label (Credit: Note.com)
Types of Autoclave:
- Autoclaves are classified based on the Heating method: Gas (use on gas burners or open fire) and Electrical (mains powered).
- By appointment, they are Home/household (usually up to 18 liters) and Industrial
- By type of coolant, they are Electric water and Steam autoclave.
- By design, they are Horizontal, vertical, rocking, Rotating, and Columned.
Procedure for Autoclaving:
- First, take out the inner sterilization chamber and then add the appropriate amount of water to it.
- Insert it back into the sterilization chamber and load the item to sterilize.
- Wrap and pack the end of the conical flask and the mouth of the test tube with a cotton plug or paper.
- Now close the autoclave lid.
- Tighten the opposite two bolts symmetrically at the same time, so that the bolts are tight and consistent, and check there is no air leakage.
- Now switch on the power supply and wait to boil the water to remove the cold air present in the autoclave chamber.
- After the cold air is completely exhausted, close the exhaust valve and allow the temperature to rise slowly as the steam pressure rises.
- Now allow steam inside to reach the desired levels generally, 121° C, for 15-20 minutes.
- Now disconnect the power supply and let the temperature in the sterilization chamber drop naturally.
- Finally, loosen the bolt, open the lid, and take out the sterilized items from the chamber.
Safety during Autoclaving:
- Strictly follow the instructions of the autoclave.
- Strictly follow the given temperature, pressure, and time during autoclaving.
- Install the autoclave only on a level surface.
- Despite the automatic process, keep an eye on the temperature and pressure.
- Always check the water level in an autoclave.
- Fill the autoclave with only 2/3 full of the water.
- It is better to use the autoclave in a ventilated area.
Precautions for using an autoclave:
The autoclave should be properly loaded to ensure that the steam can reach all instrument surfaces. It is also important to monitor the operating temperature for proper functioning. Some autoclaves have external meter readings, while others use test strips to obtain temperature readings by observing color changes. Autoclaves have the potential to explode due to improper depressurization and should be handled with care to avoid accidents.
- Do not open the autoclave until the pressure drops to 0.
- Do not use the autoclave if there is no water in the container.
- Do not use equipment with labels or stickers.
- Do not transport the equipment from place to place while it is in operation.
- Do not release pressure yourself until the temperature reaches 40 degrees.
- Do not place foreign objects on the device, do not throw them.
- Keep children and pets away from the operating autoclave
- Do not loosen bolts, nuts, etc. during operation.
- Do not touch the hot surfaces of the autoclave.
- When tightening the main bolts, they must be tightened diagonally and symmetrically several times.
- At the time of operation, it must be noted that the thermometer should be inserted into the reaction solution accurately.
- The interior of the autoclave and the gasket should be kept clean.
Autoclave Uses:
- The autoclave used for medical and health undertakings, scientific research, agriculture and other units to sterilize medical equipment, dressings, glassware, solution culture medium, etc.
- Autoclaves are widely used in medicine, especially those related to surgery, such as sterilizing instruments and discards.
- In a laboratory setting, autoclaves can be used to sterilize a variety of equipment and glassware.
- In the food industry, autoclaves are used for sterilization and pasteurization of products, as well as in the production of canned food: stew, fish, meat and vegetable and fruit preparations.
Advantages of Autoclave:
Advantages of gas autoclaves:
- They are more economical because gas is often cheaper than electricity
- They are cheaper
- Easier to operate
Advantages of electric autoclaves:
- They are lighter and less bulky
- here are special thermostats that maintain the required temperature
- Universal - i.e. they can also be used as gas, including
Advantages of electric water autoclave:
- The advantage of electric water autoclaves is that they are cheaper.
Advantages of steam autoclaves:
- They are convenient to sterilize not only glass and tin cans but also retort food.
- Saving resources.
- Faster heating and cooling of products.
- A greater degree of automation.
Advantages of vertical autoclaves:
- Currently, they are most often used in laboratories and for home preservation. Rarely - in the food industry.
- Water is heated using heating elements, which are located at the bottom of the autoclave.
- Baskets with cans are loaded from above.
Advantages of Horizontal autoclave :
- Used for industrial conservation.
- Loading of production happens sideways.
- They have better performance.
- Heat products more evenly.
- The lid closes more easily, faster, and more securely.
- They are used for sterilization of any packaging, including canned meat and other ready-to-eat food in retort packaging.
- It is possible to automate the process of loading and unloading baskets and containers with products.
Frequently Asked Questions on Autoclave:
1. What is an autoclave used for?
Answer: Autoclave is used for sterilization and disinfection of equipment, glassware, and culture medium. Autoclaves operate at high temperatures and pressure to kill microorganisms and spores.
2. What is the principle of an autoclave?
Answer: The basic principle of an autoclave is steam sterilization, which is to expose each item to direct steam contact at the required temperature and pressure for the specified time. Thus, there are four parameters of steam sterilization: steam, pressure, temperature, and time.
3. What is autoclave temperature?
Answer: The autoclave must reach and maintain a temperature of 121° C for at least 15 minutes by using saturated steam under at least 15 psi of pressure.
4. Why is it called an autoclave?
Answer: The term “Autoclave” comes from the Greek word “auto” which means self, and the Latin “clavis” meaning key, thus a self-locking device.
5. How do you sterilize equipment in an autoclave?
Answer:
- Place the items to be sterilized in the autoclave. The door is locked.
- A vacuum pump sucks the air from the chamber.
- The temperature reaches the correct level.
- Steam kills bacteria and microbes.
- Steam is released, the door is opened and items are ready for use.
6. What Cannot be sterilized in an autoclave?
Answer: In an autoclave materials that are contaminated with solvents, radioactive materials, volatile or corrosive chemicals, or items that contain mutagens, and carcinogens can't be sterilized.
7. What are the types of autoclaves?
Answer: Autoclaves are: rotating, swinging, horizontal, vertical, and column.
8. What is the difference between an autoclave and a pressure cooker?
Answer: An autoclave is generally larger than a pressure cooker, and can build up more pressure and therefore heat food to a higher temperature. However, since the dimensions of the autoclave are much larger than the pressure cooker.
9. Can the pressure cooker be used as an autoclave?
Answer: You can use the pressure cooker like an autoclave to preserve various canned food.