MCQ on DNA Replication / DNA Synthesis
Here are the MCQ on DNA Replication in Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes answers with explanations for the additional questions related to DNA Replication.
Key Points on DNA Replication:
- Semi-conservative Replication: Demonstrated first in Drosophila melanogaster, DNA replication follows a semi-conservative model, where each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
- E.coli as a Model: E.coli bacteria is commonly used in DNA replication studies due to its rapid growth and well-understood genetic makeup.
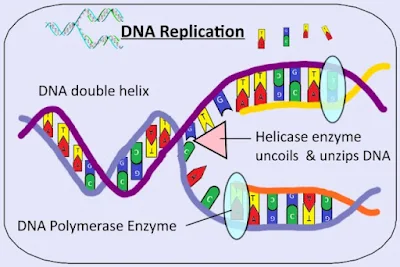
- Bidirectional and Anti-parallel: DNA replication occurs bidirectionally from the origin of replication, and the two DNA strands are anti-parallel (oriented in opposite directions).
- Chargaff's Rules: According to Chargaff's rules, the amount of purines (A and G) is equal to the number of pyrimidines (T and C) in any double-stranded DNA molecule (A + G = T + C).
- Origin of Replication: DNA replication initiates at specific sites called the origin of replication.
- Helicase and Topoisomerase: Helicase enzymes unwind and separate the DNA strands, while topoisomerase enzymes relieve supercoiling ahead of the replication fork.
- Proofreading by DNA Polymerase III: DNA polymerase III has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, allowing it to proofread newly synthesized DNA strands for errors during replication.
- Termination of Replication: Replication termination is mediated by proteins like tus Protein that act at specific sites on the DNA.
- Direction of DNA Synthesis: DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands in the 5' to 3' direction.
- Ligase and DNA Fragment Joining: Ligase enzymes are responsible for joining the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand during replication.
- Reverse Transcriptase: In certain viruses, DNA is synthesized from RNA using the reverse transcriptase enzyme, a process known as reverse transcription.
Image Source: thinkib.net
MCQ on DNA Replication in Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
1. In which of the following organisms the Semi-conservative DNA replication was first demonstrated____________
(a) Drosophila melanogaster
(b) Escherichia coli
(c) Streptococcus pneumonae
(d) Drosophila melanogaster
Answer: (d) Drosophila melanogaster
Explanation: Semi-conservative DNA replication was first demonstrated in Drosophila melanogaster by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958.
2. Which of the following bacteria is used for DNA replication studies?
(a) Neurospora crassa
(b) Drosophila melanogaster
(c) Escherichia coli
(d) Pneumococcus
Answer: (c) Escherichia coli
Explanation: Escherichia coli (E. coli) is commonly used for studying DNA replication due to its fast growth rate and well-understood genetics.
3. DNA replication is bidirectional and anti-parallel. Which of the statement is FALSE regarding the DNA replication?
(a) The DNA synthesis i.e. addition of nucleotide occurs from 5'-3' position
(b) The DNA synthesis is semi-continuous with continuous leading strand and discontinuous lagging strand.
(c) The synthesis of leading and lagging strands occurs simultaneously
(d) None of the Above
Answer: (c) The synthesis of leading and lagging strands occurs simultaneously
Explanation: The synthesis of leading and lagging strands in DNA replication occurs in opposite directions and is not simultaneous.
4. Which of the followings are the characteristic feature of DNA replication________
(a) DNA replication requires Semi conservative and Bidirectional
(b) DNA replication requires short RNA primers
(c) DNA replication is a highly accurate process
(d) All of the Above
Answer: (d) All of the Above
Explanation: DNA replication is semi-conservative, bidirectional, and highly accurate. It requires short RNA primers for initiating DNA synthesis.
Read: Biotechnology MCQ
5. The Chargaff rules state that the number of purines and pyrimidines are equal (A+G = T + C) in any double-stranded DNA molecules. Watson and Crick later solved the structure of DNA and nitrogen base pairings. Which of the following base pairing rule is true______
(a) Adenine pairs with Guanine and Thymine pairs with Cytosine
(b) Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytosine
(c) Adenine pairs with Cytosine and Guanine pairs with Thymine
(d) DNA base pairing is nonspecific
Answer: (b) Adenine pairs with Thymine and Guanine pairs with Cytosine
Explanation: The base pairing rule in DNA is specific: Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T) and Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C).
6. Eukaryotic Organisms differ from prokaryotic organisms in mechanism of DNA replication due to the____________
(a) Use of DNA primer rather than RNA primer
(b) Different enzyme for synthesis of lagging and leading strand
(c) Discontinuous rather than semi-discontinuous replication
(d) None of the above
Answer: (a) Use of DNA primer rather than RNA primer
Explanation: Eukaryotic DNA replication uses DNA primers for initiating replication, whereas prokaryotic replication uses RNA primers.
7. Which of the following protein is required for connecting Okazaki fragments?
(a) Scaffold protein
(b) Helicase
(c) Primase
(d) DNA gyrase
Answer: (d) DNA gyrase
Explanation: DNA gyrase is not directly involved in connecting Okazaki fragments. DNA ligase is the enzyme responsible for joining Okazaki fragments.
8. Which of the following protein does not involve in the initiation of replication?
(a) DnaA
(b) SSB (Single strand binding protein)
(c) DnaB
(d) DnaF
Answer: (d) DnaF
Explanation: DnaF is not a protein involved in the initiation of DNA replication. DnaA, DnaB, and SSB are involved in the initiation process.
9. What is the origin of replication?
(a) Particular site at which DNA replication starts
(b) Site which prevents initiation
(c) Random location on the DNA
(d) Site at which replication terminated
Answer: (a) Particular site at which DNA replication starts
Explanation: The origin of replication is a specific site on the DNA where replication begins. It is recognized by initiator proteins like DnaA.
10. Which of the following enzymes separates the two strands of DNA during replication?
(a) Gyrase
(b) Topoisomerase
(c) Helicase
(d) DNA polymerase
Answer: (c) Helicase
Explanation: Helicase is responsible for unwinding and separating the double-stranded DNA during replication, creating the replication fork for DNA polymerase to work on.
Read: The Living World